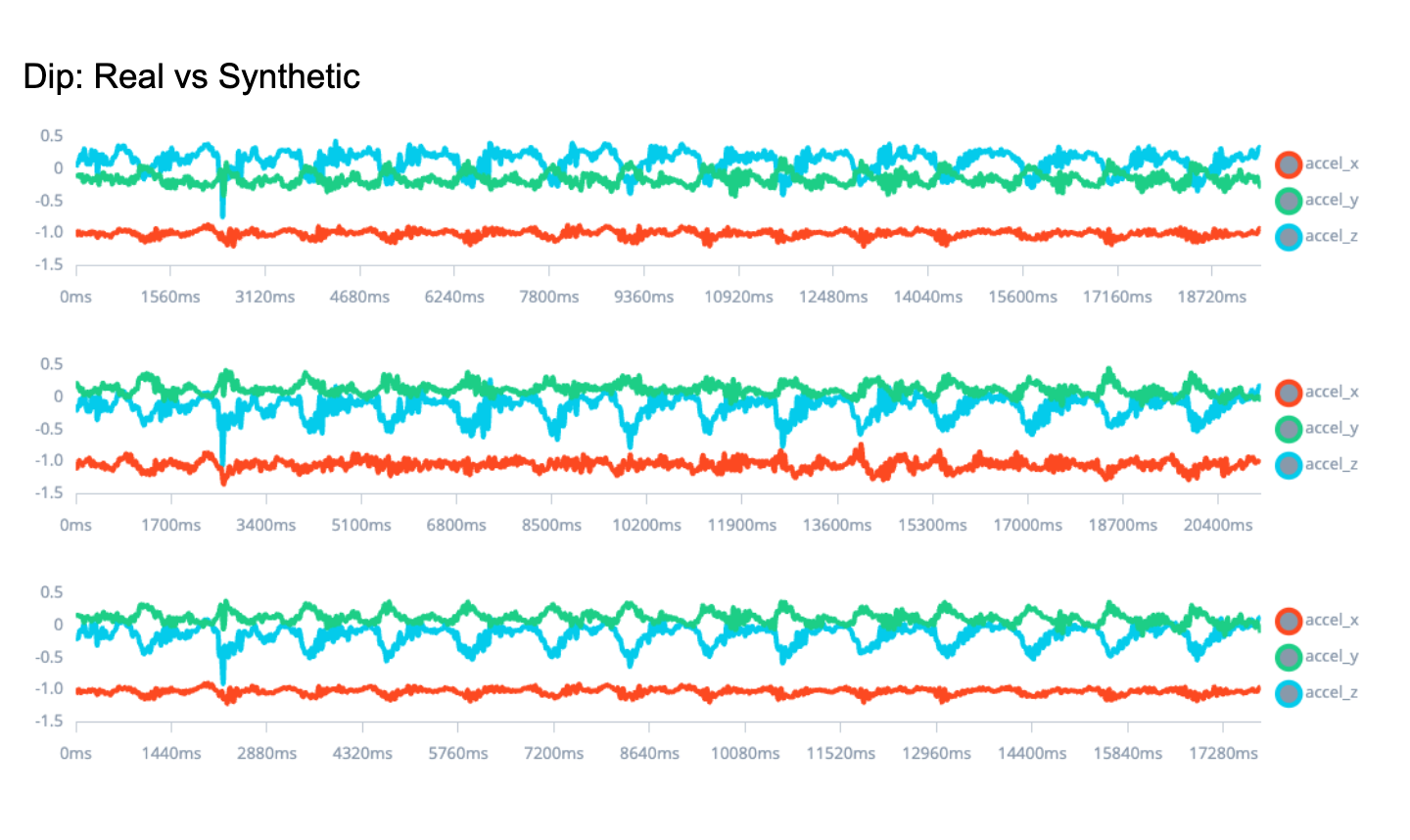
In many machine learning applications, especially those involving time series data, obtaining a large, diverse, and high-quality labeled dataset is one of the biggest hurdles. Data collection is often constrained by availability, privacy, annotation costs, and time.
To address this, data augmentation — the process of generating new data from existing samples — has become a key strategy. However, traditional augmentation methods like adding noise, scaling, or using generative models often fail to preserve the underlying structure of time series data.
Our Solution: Structure-Preserving Augmentation
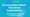
Time series data is often composed of three main components:
- Trend: Long-term progression (e.g., voltage drift in sensors)
- Seasonality: Repeating patterns (e.g., machine rotation cycles)
- Residual: Irregular short-term fluctuations (e.g., noise)
Our method decomposes a time series into these components, applies transformations to each component individually, and then reconstructs a new series. This ensures the augmented data retains the structural integrity of the original.
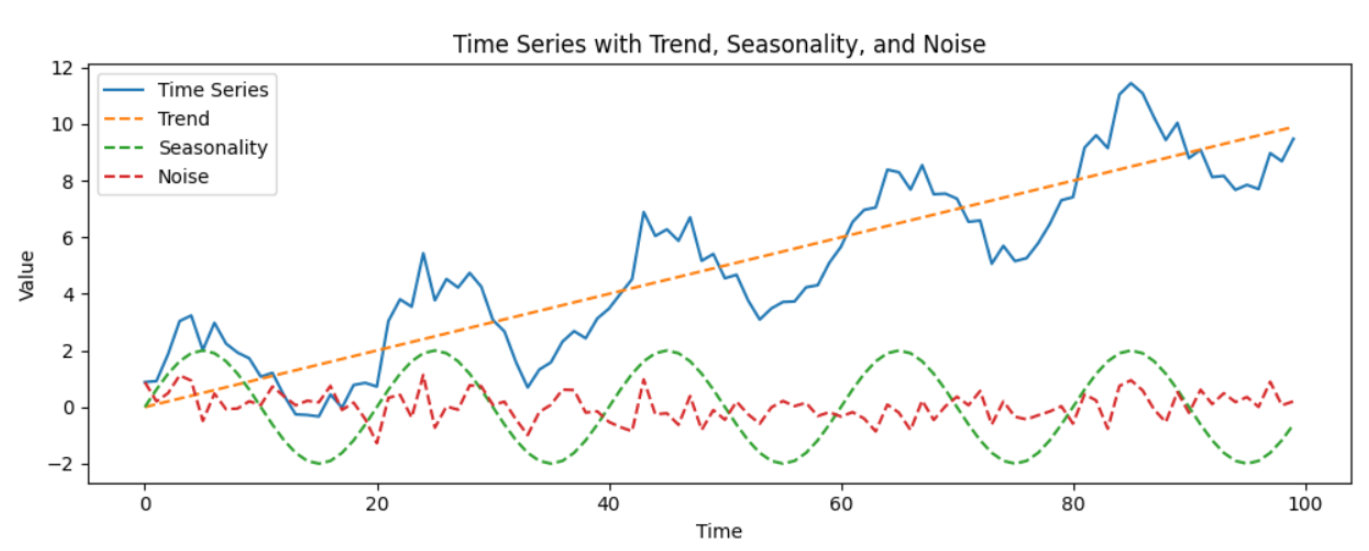
Layer 1: Transforming Components from the Same Series
In the first layer, we take a single time series and decompose it using techniques like Seasonal-Trend Decomposition using Loess (STL). We then apply transformations such as:
- Amplitude scaling (e.g., increase trend magnitude)
- Time scaling (e.g., compress or stretch the seasonal cycle)
- Synchronized slicing (reorder cycles of the seasonal component with smooth transitions)
Finally, we recombine the transformed components to synthesize a new time series.
This approach allows us to generate realistic variations while preserving the original structure.
Layer 2: Mix-Matching Components from Different Series
If we have multiple time series from similar sources (e.g., different machines of the same origin), we can further expand our augmentation by mixing components across series. For example:
- Use the trend from Series A
- Combine it with the seasonality from Series B
- Add the residual from Series C
This creates a new series that is structurally valid but more diverse than any individual source.
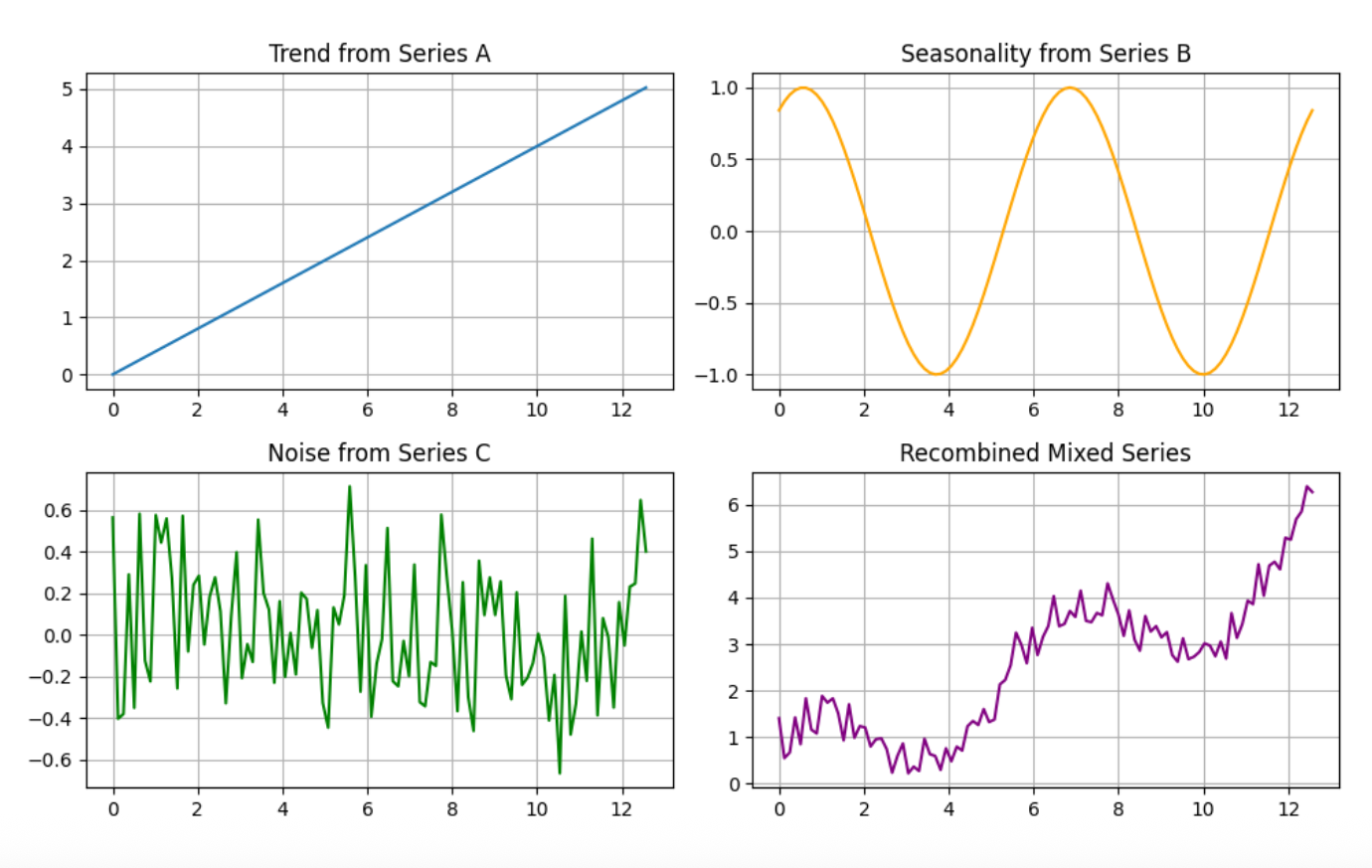
This second layer significantly increases the variety of the augmented dataset while maintaining coherence.
Smart Automation and Simple Control
To make this solution both powerful and easy to use, we introduce two key features:
- Automatic Decomposition Strategy Depending on the characteristics of the time series, the system automatically chooses between:
a. STL decomposition for series with strong seasonality
b. Wavelet decomposition for series without clear seasonal patterns
This decision is based on the energy in the seasonal component, compared against an empirically determined threshold.
- Single “Divergence” Parameter Instead of manually tuning multiple augmentation parameters, users can adjust a single “divergence” setting. Internally, this controls:
a. Amplitude and time scaling
b. Whether to apply slicing or remixing
c. Degree of transformation per component
This makes the solution accessible to non-experts while still offering the flexibility and power needed by advanced users.
Why It Matters
This decomposition-based augmentation strategy — developed and delivered by Edge Impulse — offers a scalable, structure-aware, and user-friendly way to generate realistic synthetic data , improving model robustness and reducing costly data collection.
Whether you're working with sensor data, industrial signals, or any other time series, this approach helps you get more value from the data you already have.
Best Practice
- Best suited for consistent, single-label samples This approach performs optimally when samples have uniform characteristics, with each labeled with a single class.
- High-quality input data is essential Use clean, representative example samples — poor data leads to poor results. "Garbage in, garbage out" still applies.
- Start small and iterate Begin with a small number of outputs and low divergence setting, and gradually explore the impact of tuning parameters.
- We're here to support your journey Whether you're debugging or scaling up, don't hesitate to reach out — we're always ready to assist.
Example Project